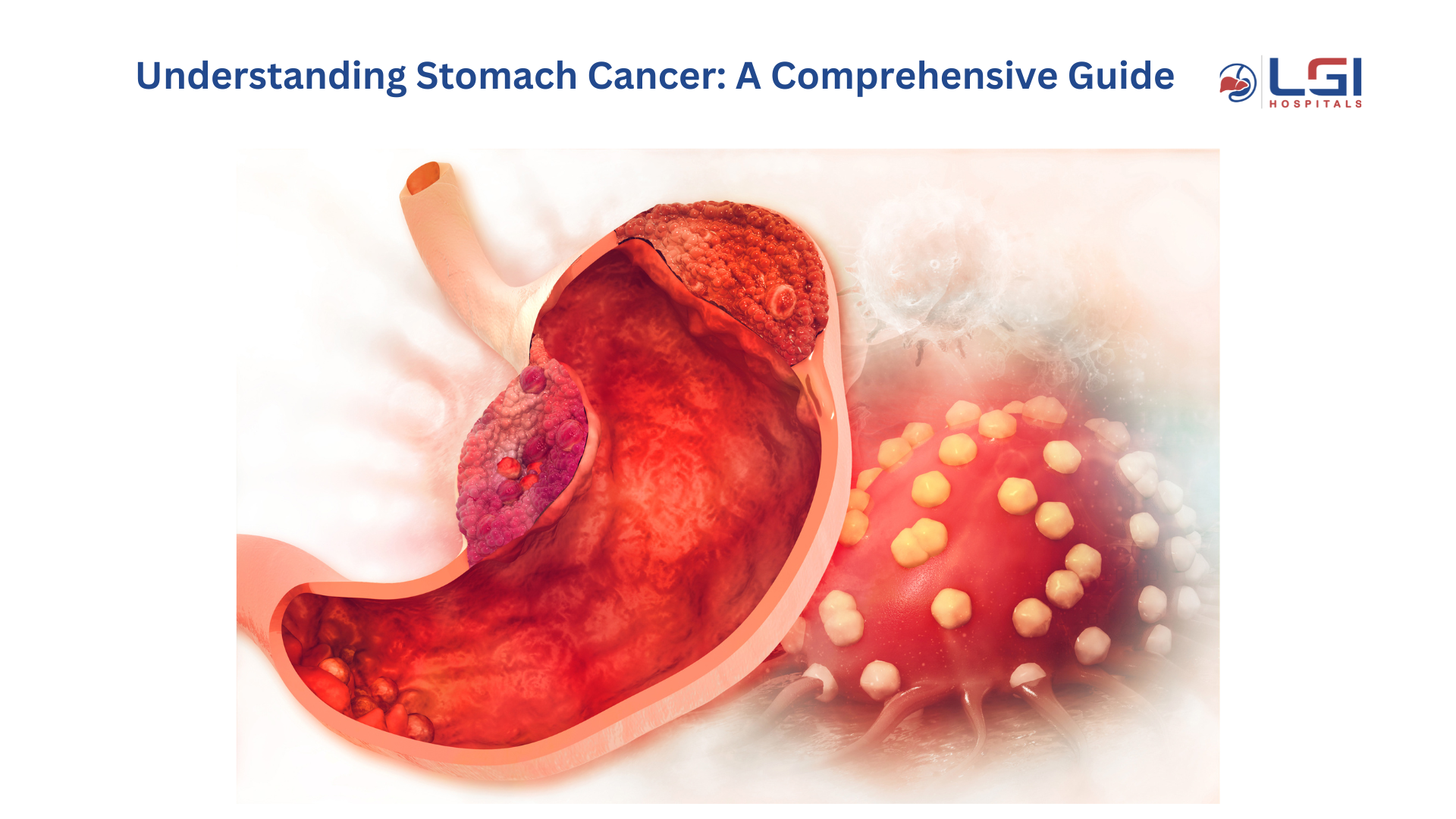
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a type of cancer that begins in the cells lining the stomach. It is a significant global health issue, with varying rates of incidence in different regions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for stomach cancer.
What is Stomach Cancer?
Cancer occurs when malignant (cancerous) cells form in the lining of the stomach. There are several types of stomach cancer, with adenocarcinoma being the most common, accounting for about 90-95% of cases. Other types include lymphomas, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), and carcinoid tumors.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of stomach cancer is not always clear, but several risk factors have been identified:
Helicobacter pylori infection: Chronic infection with this bacteria is a major risk factor.
Diet: High intake of smoked, salted, or pickled foods can increase risk, while a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can lower it.
Smoking: Smokers are more likely to develop stomach cancer than non-smokers.
Genetics: A family history of cancer can increase risk.
Other medical conditions: Conditions like chronic gastritis, pernicious anemia, and gastric polyps can increase the risk.
Stomach Cancer Symptoms
Early-stage cancer rarely causes symptoms, making it difficult to detect. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
– Persistent stomach pain or discomfort
– Unexplained weight loss
– Nausea and vomiting, sometimes with blood
– Difficulty swallowing
– Loss of appetite
– Bloating after meals
– Blood in stools or black stools
– Fatigue and weakness
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice.
Diagnosis of stomach cancer
Diagnosing involves several steps:
1. Medical History and Physical Exam: Doctors will first take a thorough medical history and perform a physical examination.
2. Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to view the stomach lining and take biopsies.
3. Imaging Tests: Tests such as CT scans, PET scans, and X-rays help determine the extent of cancer spread.
4. Biopsy: Samples of stomach tissue are examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Stomach Cancer Treatment
Treatment options for stomach cancer depend on the stage of the disease, the location of the tumor, and the patient’s overall health.
Common treatments include:
Surgery: Surgery is a primary treatment for stomach cancer. It may involve removing part of the stomach (partial gastrectomy) or the entire stomach (total gastrectomy).
Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be given before surgery (neoadjuvant) to shrink tumors or after surgery (adjuvant) to kill remaining cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is often combined with chemotherapy.
Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells with certain genetic changes.
Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Prevention of stomach cancer
While there is no sure way to prevent cancer, certain lifestyle changes can reduce your risk:
Healthy Diet: Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, and limit intake of salty, smoked, and pickled foods.
Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco in all forms.
Limit Alcohol: Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all.
Treat Helicobacter pylori Infection: If diagnosed with H. pylori infection, appropriate treatment can reduce risk.
Regular Screening: For those at high risk (family history or genetic predisposition), regular screening can help in early detection.
Stomach cancer is a serious condition, but advancements in medical research and treatment options offer hope for patients. Understanding the risk factors, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely medical care can significantly improve outcomes.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of stomach cancer, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment plan. Early detection and intervention are key to managing stomach cancer effectively.
For expert care and support, trust the experienced team at LGI Hospital, where we are dedicated to providing comprehensive and compassionate care for all our patients.